Acetylcholine: A Neurotransmitter
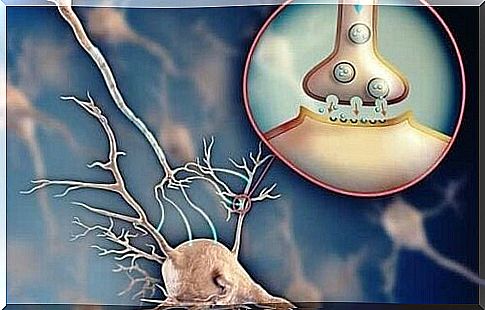
Acetylcholine is the most abundant neurotransmitter in our nervous system. This compound, which our brains produce primarily through sugar and choline, is an essential messenger in the brain that promotes communication between nerve cells. It participates in the regulation of attention and memory function, as well as in the assimilation of new knowledge. It also helps us take care of our mood.
It should be mentioned at the outset that acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter to be detected. The subject was first studied by Henry Hallett Dale in 1915. Later, Dr. Otto Loewi described much of the functions of acetylcholine. Both of these studies received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1936. As you can see, this is not just any chemical combination: the importance of this small substance to human life and our vital functions is enormous.
For example, it is known that there are certain cells in our body that react exclusively to acetylcholine. Consider even the forebrain and the hippocampus, which specifically need this neurotransmitter to produce their functions.
Acetylcholine not only acts as a messenger, but also enhances the intensity of intercellular messages via theta waves. It enhances memory and promotes brain plasticity and communication. Let’s take a closer look at this below .
What are the functions of acetylcholine?
Many have heard of acetylcholine for one specific reason: its role in improving memory and concentration. This is why it is one of the most common compounds in nootropins, substances used to enhance intellectual performance. But in addition to this, it is known that it is necessary for many other functions, which will be considered below.
It should be mentioned at the outset that the areas of action of acetylcholine in our body are diverse. It is present in both the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system, and in addition it has both accelerating and decelerating effects. Thus, it can accelerate an electrical impulse in a nerve cell, or block the heart rate in certain situations. It’s like a conductor who leads an orchestra and makes sure that each function has a certain rhythm, harmony and balance.
Functions of acetylcholine in the central nervous system
In the central nervous system, acetylcholine acts as an accelerator. It promotes motivation, agitation, and alertness through its interaction with nerve cells, or neurons. Not only does it stimulate the hippocampus to implement those processes, but it also affects the cerebral cortex and, through it, higher-level conscious action control, such as problem solving or reflection.
On the other hand, decreased function of cholinergic neural pathways in the central nervous system and loss of communication between them are associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Acetylcholine and REM sleep
This is interesting information: acetylcholine promotes REM sleep by focusing on a very specific part of our brain, the forebrain. Falling into REM sleep (paradoxical sleep, blinking) helps the brain store the knowledge and skills learned during the day.
Hormone function
Some of the neurotransmitters in our brain, such as oxytocin, are also hormones. Acetylcholine also has an important hormonal function: it affects the pituitary gland. Thus, for example, it can control the amount of urine excreted, stimulate the production of thyroid hormones, etc.
Functions of acetylcholine in the peripheral nervous system
Without acetylcholine, our peripheral nervous system would not be able to perform much of its function. These tasks are quite diverse and important for our survival and well-being:
- It conveys a message between our brains and the muscles of the heart.
- It is also a bridge between our brains, nerves, muscles and bones, and here it is its job to participate in the formation of each of our movements.
- In the heart and circulatory system, it almost always acts to dilate blood vessels, that is, it lowers and evens out the heart rate.
- In the digestive system, it promotes intestinal contractions.
- In the urinary tract, it triggers the voluntary removal of urine.
Acetylcholine is also involved in a process that is important for survival: feeling pain.
How can acetylcholine production be promoted?
As mentioned at the beginning, our brains need sugar to produce acetylcholine. However, it is important to stay moderate in your use of sugar, as it often happens that after eating large amounts of sweets, our attention and memory function deteriorates within a couple of hours. Why is this happening? Excessive sugar causes the excretion of adenosine. This in turn inhibits the action of acetylcholine.
So following a balanced diet is always best. In addition, if we want to increase the production of this neurotransmitter in our body, the best way is to add the following foods for daily use:
- A cup of coffee
- Soy lecithin
- Cinnamon
- Rosemary
- Red grapes
- Egg yolk
- Wheat germ
- Broccoli
- Banana
- Peanut
- Orange
- Oats
- Flax seeds

It is amazing how some of the substances so unknown, enigmatic and unique in our bodies can do so much for us. So now that we know the importance of acetylcholine, let us also try to take care of its balance in our body. Let’s remember the importance of a healthy diet as well as an active lifestyle, not forgetting regular health checkups to make sure everything is in order.